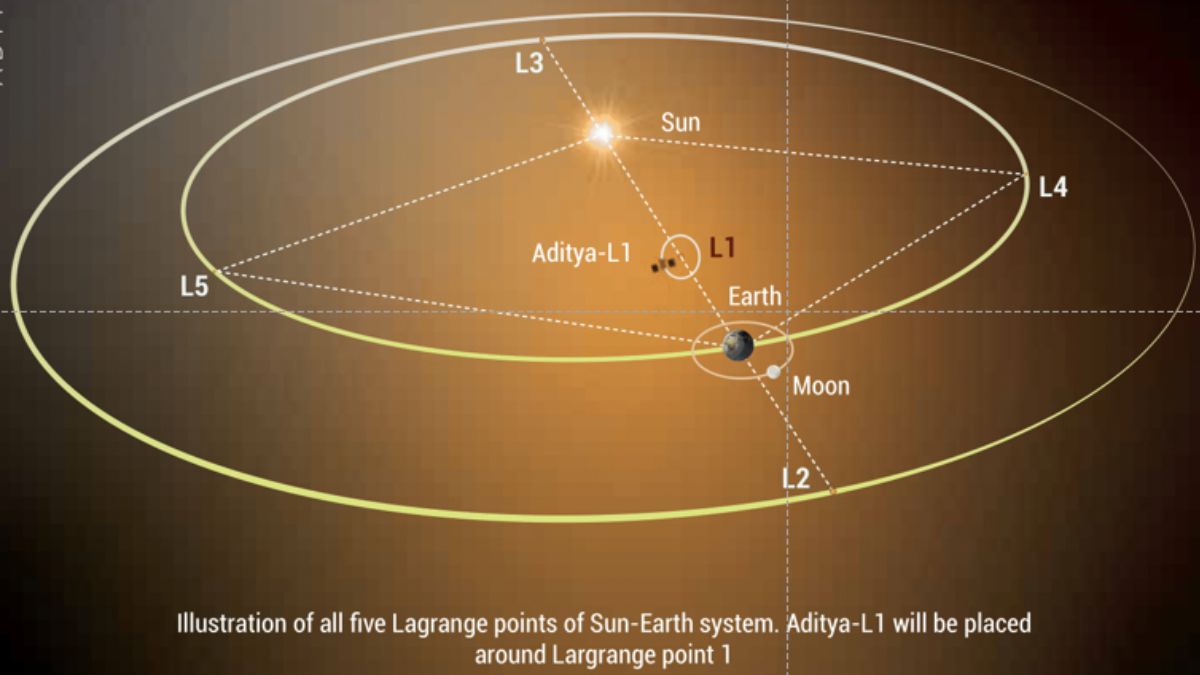
The ISRO on Saturday successfully launched India’s first solar explorer, the Aditya L1, aboard its PSLV-C57 launch vehicle from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Andhra Pradesh’s Sriharikota. The solar probe will be placed in the halo orbit around the Sun-Earth system’s Lagrange 1 (L1) point. The first Indian space-based observatory to study the Sun will stay approximately 1.5 million km away from Earth, which is about 1% of the Earth-Sun distance, ISRO said.
The spacecraft will conduct several in-situ experiments as part of the solar exploration mission. According to ISRO, Aditya-L1 is carrying seven payloads to observe the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona (the Sun’s outermost layer) using electromagnetic and particle, and magnetic field detectors.
“Using the special vantage point L1, four payloads [will] directly view the Sun and the remaining three payloads [will] carry out in-situ studies of particles and fields at the Lagrange point L1, thus providing important scientific studies of the propagatory effect of solar dynamics in the interplanetary medium,” the national space agency stated.
The following are the stated objectives of the spacecraft:
– To study the dynamics of the two upper layers of the Sun’s atmosphere – chromosphere and corona.
– To study chromospheric and coronal heating, partially ionized plasma physics, coronal mass ejections initiation, and solar flares.
– Observe the in-situ particle and plasma environment providing data for the study of particle dynamics from the Sun.
– To study the of solar corona and its heating mechanism.
– Diagnose coronal loops plasma: Temperature, velocity and density.
– To study the development, dynamics and origin of coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
– Identify the sequence of processes that occur at multiple layers (chromosphere, base and extended corona) which eventually leads to solar eruptive events.
– Magnetic field topology and magnetic field measurements in the solar corona.
– To study the drivers for space weather (origin, composition and dynamics of solar wind).
“The suits of Aditya L1 payloads are expected to provide most crucial informations to understand the problem of coronal heating, coronal mass ejection, pre-flare and flare activities and their characteristics, dynamics of space weather, propagation of particle and fields etc,” ISRO said in an official release.




